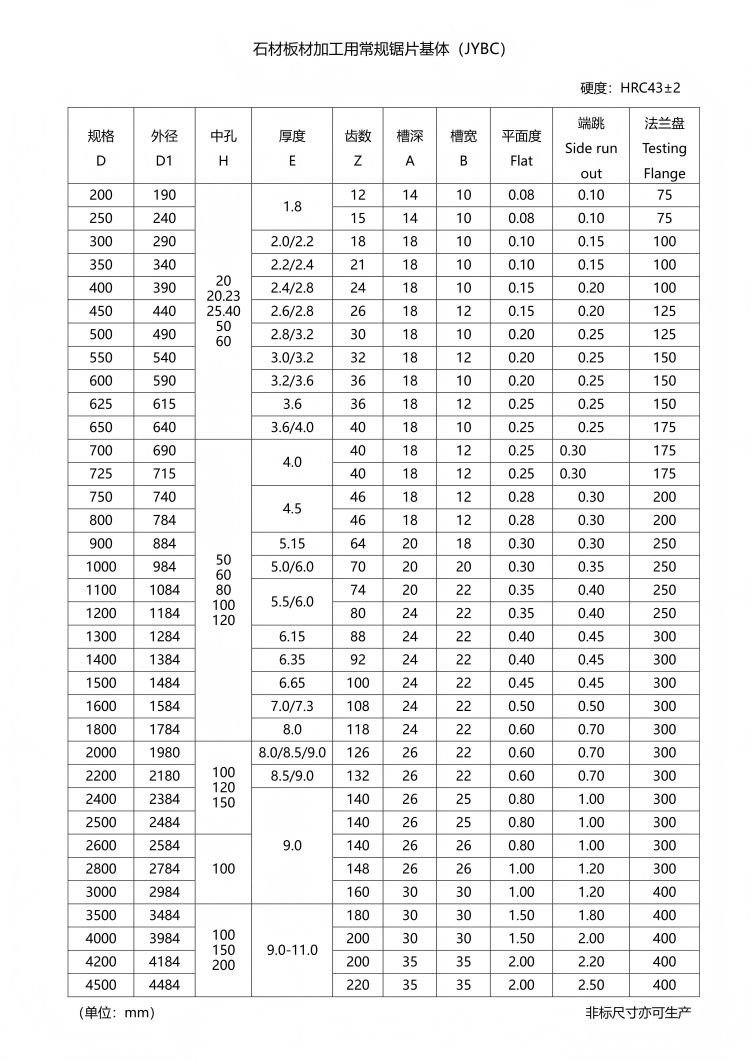
Normal Saw Blanks
Diamond saw blanks for stone (Normal Saw Blanks) are a widely used standard type of diamond saw blade for stone cutting and processing. Their key features include even hardness, wear resistance, and cutting performance, making them suitable for continuous cutting tasks involving common stones such as granite and marble.
• Blanks material: Typically made from 65Mn spring steel or 75Cr1 alloy steel, undergoes precision machining and heat treatment (quenching + tempering) to ensure high strength and fatigue resistance.
• Diamond tip welding method: Laser welding/high-frequency welding ensures a secure bond between the diamond tips and the base.
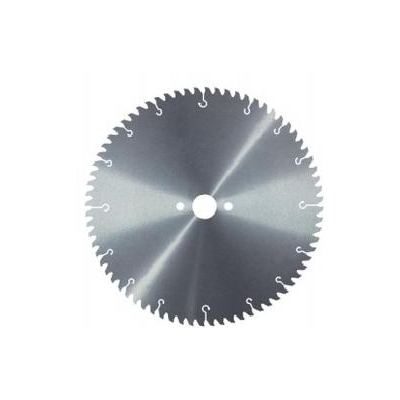
·Tooth shape: Generally uses continuous teeth or block-type (uniform blade spacing) to accommodate different hardness levels of stone.
·Heat dissipation design: The base features heat dissipation holes or pressure relief grooves to reduce thermal deformation and stress concentration.
Diamond saw blades for stone (standard blades) are a widely used standard type of diamond saw blade for stone cutting and processing. Their key features include balanced hardness, wear resistance, and cutting performance, making them suitable for continuous cutting tasks involving common stones such as ordinary granite and marble.
• Base material: Typically made from 65Mn spring steel or 75Cr1 alloy steel, undergoes precision machining and heat treatment (quenching + tempering) to ensure high strength and fatigue resistance.
• Diamond tip welding method: Laser welding/high-frequency welding ensures a secure bond between the diamond tips and the base.
·Tooth structure: Generally uses continuous teeth or block-type (uniform blade spacing) to accommodate different hardness levels of stone.
·Heat dissipation design: The base features heat dissipation holes or pressure relief grooves to reduce thermal deformation and stress concentration.
2. Main applications of conventional blades
(1) Cutting ordinary granite and marble
• Block sawing: Cutting large blocks of quarried stone into workable blocks.
• Slab cutting: Used in bridge saws, gantry saws, and other equipment to cut stone into slabs (thickness 10 mm–50 mm).
• Curbstone/sidewalk stone: Processing stone for municipal engineering projects.
(2) Processing of medium-hardness stone
• Suitable for sandstone, limestone, slate, etc., but not suitable for ultra-hard stone (such as black granite, basalt).
(3) Stone Edge Trimming and Secondary Processing
• Used for trimming rough edges and cutting corners, particularly suitable for softer stones like marble and engineered quartz.
(4) Concrete Cutting at Construction Sites
• Can cut plain concrete and lightweight bricks, but the feed speed must be reduced to extend tool life.
3. Main advantages of conventional films
Advantages | Detailed description |
Highly versatile | Suitable for most medium-hardness stones, such as granite, marble, sandstone, etc., with wide market application. |
High cost performance | Compared to high-end saw blades, the price is moderate, suitable for small and medium-sized stone factories and batch processing. |
Stable cutting | The substrate is rigid and resistant to deformation, ensuring a flat cutting surface and reducing chipping. |
Easy to maintain | Using conventional welding technology, the blade head can be re-welded and repaired, reducing usage costs. |
Good heat dissipation | The optimally designed heat dissipation slots reduce the impact of high temperatures and extend the life of the saw blade. |